rockwel hardness test formula|rockwell hardness testing chart : importer There are several alternative scales, the most commonly used being the "B" and "C" scales. Both express hardness as an arbitrary See more WEBSegue as aventuras de Yuji e de seus colegas de feitiçaria Jujutsu quando uma cortina de repente cai ao redor da estação de Shibuya. Com flashbacks de Gojo e Geto enquanto .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Animais Pets. Esportes e Lazer. Para sua casa. Eletrônicos e celulares. Música e hobbies. Bebês e crianças. Veículos e barcos. Imóveis. Moda e beleza. Empregos e serviços. .
The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different . See moreThe differential depth hardness measurement was conceived in 1908 by Viennese professor Paul Ludwik in his book Die Kegelprobe (crudely, "the cone test"). The differential-depth method . See moreThe Rockwell hardness test can be conducted on several various hardness testers. All testers, however, fall under one of three categories. Bench model hardness testers can be found . See more
greenscapes digital moisture meter watering guide
There are several alternative scales, the most commonly used being the "B" and "C" scales. Both express hardness as an arbitrary See more• International (ISO)• US standard (ASTM International) See more
• Brinell hardness test• Hardness comparison• Holger F. Struer• Knoop hardness test See more• Video on the Rockwell hardness test• Hardness Conversion Chart• Rockwell to brinell conversion chart• Hardness Conversion Table See moreRockwell hardness test measures the permanent depth of indentation on the material by applying a fixed load using an indenter. The smaller the indentation value, the harder is the material. The Rockwell hardness test follows the .
Rockwell Hardness Test Formula. Rockwell hardness test is directly read from the equipment. However, there is a formula to convert the measured depth (d) into the Rockwell hardness number. A Rockwell hardness number for a .Preliminary test loads (preloads) range from 3 kgf (used in the “Superficial” Rockwell scale) to 10 kgf (used in the “Regular” Rockwell scale). Total test forces range from 15kgf to 150 kgf (superficial and regular) to 500 to 3000 kgf .
Where HR is the Rockwell hardness value, N is the load applied (in kgf), d is the depth of the indentation (in mm), and D is the diameter of the ball or the width of the diamond cone (in mm). The Rockwell hardness test uses .The Rockwell hardness test measures hardness in progressive numbers on different scales corresponding to the size of ball indentor used; scale symbols correspond to the loads of 60 . The Rockwell hardness test is the industry standard measuring system used to determine how resistant a material is to another object. Hardness is defined as a material’s resistance to permanent indentation. This test was .The process is used to test hardness in the macro range (test force >= 49.03 N), more precisely with a test force of 29.42 to 1471 N. It is a differential-depth method. This means that the residual depth of indentation left by the indenter .
The Rockwell Hardness test is a widely used method to determine the hardness of metallic materials, thanks to its simplicity and quickness. This hardness test is based on .The Rockwell hardness test is used for macro hardness tests, which are generally defined as tests that use indentation loads below or equal to 1 kgf. Therefore, a ground surface is usually sufficient, and sometimes no .
The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method. You should obtain a copy of this standard, read and understand the standard completely before attempting a .
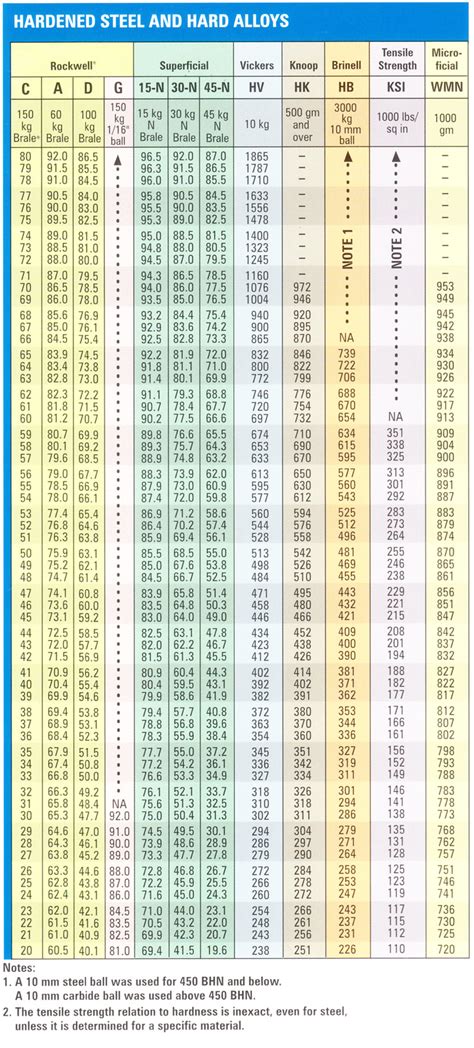
1. Define Hardness. 2. Applications of Rockwell Hardness A ± Scale, B-Scale, C-Scale. 3. Type of Indentor used in the Three Different Scales of Rockwell Hardness Test. 4. Different Types of Hardness Testing Methods. 5. Size of the Ball to be used in Ball Indentor of Rockwell Hardness Test. 6. Di ameters of the different Balls used in Brinell .Rockwell testing falls into two categories: Regular Rockwell testing (e.g., C and B scales) and Rockwell superficial testing (e.g., 30 N and 30 T scales). High Rockwell hardness numbers represent hard materials and low numbers soft materials. d 2 www.wilsoninstruments.com Fundamentals of Rockwell Hardness TestingII. Theory and Principle of the Rockwell Hardness Test. The Rockwell Hardness Test uses a depth-differential method to test for hardness. A predetermined minor load is applied to the test sample, and the depth measurement is taken. Then a major load is applied to the same spot, which creates a deeper indentation.
A widely used variant of the Rockwell hardness test is the superficial Rockwell test, wherein the minor load is 3 N and the major loads are 15, 30, or 45 N.Further details on the Rockwell superficial hardness scales are available in the relevant ASTM standards (ASTM 1984).The Rockwell hardness values are expressed as a combination of hardness number and a scale .This first load is removed, and another heavier load is applied to the indenter on the test piece. The Rockwell hardness of the test piece is calculated by subtracting the second load from the first and using the Rockwell formula. The resulting value is then translated to the Rockwell C scale of hardness to determine the hardness of the material. The formula for Rockwell hardness is as follows: HR = N – (d / D) . The Rockwell hardness test is widely used to measure the hardness of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. To apply the formula for Rockwell hardness, you will need to have the following information: The load applied (in kgf)
Performing hardness testing can take many forms, depending on the protocols followed. There are many hardness scales and one of the most common is the Rockwell scale. To convert Rockwell Hardness to Tensile Strength, use a polynomial equation developed by modeling the tested materials. The general formula is: TS = c3 * RH^3 + c2 * RH^2 + c1 .For instance, converting from a Rockwell hardness test on the C scale (HRC) to a Brinell hardness test value requires using the formula: BHN = 5.970 x (HRC + 104.7). This formula gives an approximate value for the Brinell hardness value, and quality assessment professionals use it to create the conversion tables and charts for instant conversion.Rockwell hardness test for plastics: In this test, a load of 15 or 30 kg is applied to the surface of the plastic material for a few seconds. . Using the formula for the Rockwell C scale, we can calculate the Rockwell hardness number (RHN) as: RHN = 100 – (d / 0.002mm) RHN = 100 – (0.8 mm / 0.002mm) RHN = 100 – 400 RHN = -300 Note: In .
Figure 1. An operator performing a Rockwell hardness test. (Source: Arkansas Department of Transportation.) The Rockwell hardness is calculated using the following formula: Rockwell Hardness, HRC = [0.2 – permanent depth of indentation (mm)] x 500. The Rockwell hardness test was developed to be less destructive and cheaper than the Brinell test.
Rockwell Hardness Testing Reference Guide ASTM E18 contains a listing of all regular Rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are applicable. Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your application. Regular Rockwell Testing. In this test method, the minor (preload) is always 10 kgf. .The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method. The Rockwell test is generally easier to perform and more accurate than other hardness methods. The Rockwell test method is used on all metals except in circumstances where the test metal structure or surface condition would introduce too .
The Rockwell hardness test is an empirical indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, and other physical characteristics . Rockwell hardness testing can determine the hardness of most metals, alloys and plastics, ranging from the softest bearing materials to the hardest steels. Photo: Wilson Instruments, An Instron Company . In the HRC . The equation for the Rockwell hardness test for metals is below: d=depth from zero load point. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. Rockwell A scale. Used to test: Tungsten carbide. Rockwell .See also: Hardness. Rockwell Hardness Test. Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload .
The Vickers hardness test is a macro and microhardness testing method, while the Rockwell test is used only as a macro testing method. The Rockwell test is a quick and direct process, while the Vickers hardness test is a slow process and requires other optical devices such as a microscope to measure the hardness of the object. Related Article . Rockwell Hardness Scale. The Rockwell Hardness Scales comprise various types, depending on the material to be tested. Each scale utilizes different loads or indenters, and permits the testing of materials with different hardness. For instance, the HRB scale is employed for testing soft steels, aluminium, and brass, and involves applying minor .EXAMPLE 70 HR30N = Rockwell superficial hardness of 70 measured on the 30 N scale with a total test force of 294,2 N. 4.4 The Rockwell superficial hardness for the T scale is denoted by the symbol HR preceded by the hardness
Common indentation hardness scales are Brinell, Rockwell and Vickers. See also: Hardness. Rockwell Hardness Number – Rockwell Scale. Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an .The Rockwell hardness test is one of several common indentation hardness tests used today, other examples being the Brinell hardness test and Vickers hardness test. Most indentation hardness tests are a . hardness is calculated using a formula that was derived to yield a number falling within an arbitrarilyMetallic materials — Rockwell hardness test — Part 2: Verification and calibration of testing machines and indenters 1 Scope This document specifies two separate methods of verification of testing machines (direct and indirect) for determining Rockwell hardness in accordance with ISO 6508-1, together with a method for verifying The formula is: Brinell Hardness (HB) = Load (kgf) / (Pi * Indentation Diameter^2). What are the disadvantages of Rockwell? The Rockwell hardness test can be influenced by surface conditions and is not suitable for very thin or small specimens. It can also be sensitive to vibrations and needs careful calibration. . HRC (Rockwell C) is a .
3.1. Rockwell Hardness Test. . The final Knoop hardness (HK) is derived from the following formula: HK = 14.229(F/D2), with F being the applied load (measured in kilograms-force) and D2 the area of the indentation (measured in square millimetres). Knoop hardness numbers are often cited in conjunction with specific load values. The Rockwell hardness test involves making an indentation on the test material. The indenter is either a conical diamond or a steel ball. Indenter ball diameters range from 1/16 to 1/2 inches and are chosen based on the test parameters.
rockwell hardness testing chart
webIMVU CUSTOM PLUGS. HOME. Example Page (BE SURE TO CLICK) CONTACT. More. STOLEN IMVU CUSTOMS Any imvu custom stolen for you for the right price. “Most .
rockwel hardness test formula|rockwell hardness testing chart